字数统计:
6.9k字
|
阅读时长:
29分
面向对象 成员变量和局部变量的区别 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Varialbe int num; public void show() { int num2 = 20 ; System.out.println(num2); System.out.println(num); } } class VariableDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Varialbe v = new Varialbe(); System.out.println(v.num); v.show(); } }
方法的形式参数是类名的时候如何调用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Demo public int sum(int a,int b) { return a + b; } } class Student public void show() { System.out.println("我爱学习" ); } } class StudentDemo public void method(Student s) { s.show(); } } class ArgsTest public static void main(String [] args) { Demo d = new Demo(); int result = d.sum(10 ,20 ); System.out.println("result:" +result); System.out.println("--------------" ); StudentDemo sd = new StudentDemo(); Student s = new Student(); sd.method(s); } }
匿名对象的概述和应用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Student public void show() { System.out.println("我爱学习" ); } } class StudentDemo public void method(Student s) { s.show(); } } class NoNameDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.show(); s.show(); System.out.println("--------------" ); new Student().show(); new Student().show(); System.out.println("--------------" ); StudentDemo sd = new StudentDemo(); sd.method(new Student()); new StudentDemo().method(new Student()); } }
封装和private 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 封装(理解) (1 )隐藏实现细节,提供公共的访问方式 (2 )好处: A:隐藏实现细节,提供公共的访问方式 B:提高代码的复用性 C:提高代码的安全性 (3 )设计原则 把不想让外界知道的实现细节给隐藏起来,提供公共的访问方式 (4 )private是封装的一种体现。 封装:类,方法,private修饰成员变量 private关键字(掌握) (1 )私有的意义,可以修饰成员变量和成员方法 (2 )特点: 被private修饰的后的成员只能在本类中被访问 (3 )private的应用: 以后再写一个类的时候: 把所有的成员变量给private了 提供对应的getXxx()/setXxx()方法
private的引出 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 class Student String name; private int age; public void setAge(int a) { if (a < 0 || a > 120 ) { System.out.println("你给的年龄有问题" ); }else { age = a; } } public void show() { System.out.println("姓名:" +name); System.out.println("年龄:" +age); } } class StudentDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.show(); System.out.println("--------------" ); s.name = "林青霞" ; s.setAge(27 ); s.show(); System.out.println("--------------" ); s.setAge(-27 ); s.show(); System.out.println("--------------" ); } }
private关键字的概述和特点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Demo private int num = 10 ; public void show() { System.out.println(num); } private void method() { System.out.println("method" ); } public void function ( method(); } } class PrivateDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Demo d = new Demo(); d.show(); d.function ( } }
private的应用标准案例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class Student private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String n) { name = n; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int a) { age = a; } } class StudentTest public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); System.out.println(s.getName()+"---" +s.getAge()); s.setName("林青霞" ); s.setAge(27 ); System.out.println(s.getName()+"---" +s.getAge()); } }
this关键字的概述和应用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Student private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this .name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this .age = age; } } class StudentTest public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.setName("林青霞" ); s.setAge(27 ); System.out.println(s.getName()+"---" +s.getAge()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Student private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this .name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this .age = age; } } class StudentTest2 public static void main(String [] args) { Student s1 = new Student(); s1.setName("林青霞" ); s1.setAge(27 ); System.out.println(s1.getName()+"---" +s1.getAge()); Student s2 = new Student(); s2.setName("刘意" ); s2.setAge(30 ); System.out.println(s2.getName()+"---" +s2.getAge()); } }
this关键字的内存图解
标准手机类代码及其测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Phone private String brand; private int price; private String color; public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this .brand = brand; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this .price = price; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this .color = color; } } class PhoneTest public static void main(String [] args) { Phone p = new Phone(); System.out.println(p.getBrand()+"---" +p.getPrice()+"---" +p.getColor()); p.setBrand("三星" ); p.setPrice(2999 ); p.setColor("土豪金" ); System.out.println(p.getBrand()+"---" +p.getPrice()+"---" +p.getColor()); } }
构造方法概述和格式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Student private String name; private int age; public Student() { System.out.println("这是构造方法" ); } } class ConstructDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); System.out.println(s); } }
构造方法的重载及注意事项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 class Student private String name; private int age; public Student() { System.out.println("这是无参构造方法" ); } public Student(String name) { System.out.println("这是带一个String类型的构造方法" ); this .name = name; } public Student(int age) { System.out.println("这是带一个int类型的构造方法" ); this .age = age; } public Student(String name,int age) { System.out.println("这是一个带多个参数的构造方法" ); this .name = name; this .age = age; } public void show() { System.out.println(name+"---" +age); } } class ConstructDemo2 public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.show(); System.out.println("-------------" ); Student s2 = new Student("林青霞" ); s2.show(); System.out.println("-------------" ); Student s3 = new Student(27 ); s3.show(); System.out.println("-------------" ); Student s4 = new Student("林青霞" ,27 ); s4.show(); } }
成员方法的分类及使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 class Student public String getString() { return "helloworld" ; } public void show() { System.out.println("show" ); } public void method(String name) { System.out.println(name); } public String function (String s1,String s2 ) return s1+s2; } } class StudentDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.show(); String result = s.getString(); System.out.println(result); s.method("林青霞" ); String result2 = s.function ("hello" ,"world" System .out .println (result2 ); } }
一个标准学生类的代码及测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 class Student private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name,int age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this .name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this .age = age; } public void show() { System.out.println(name+"---" +age); } } class StudentTest public static void main(String [] args) { Student s1 = new Student(); s1.setName("林青霞" ); s1.setAge(27 ); System.out.println(s1.getName()+"---" +s1.getAge()); s1.show(); System.out.println("----------------------------" ); Student s2 = new Student("刘意" ,30 ); System.out.println(s2.getName()+"---" +s2.getAge()); s2.show(); } }
一个标准手机类的代码及测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Phone private String brand; private int price; private String color; public Phone() {} public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this .brand = brand; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this .price = price; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this .color = color; } } class PhoneTest public static void main(String [] args) { Phone p = new Phone(); p.setBrand("诺基亚" ); p.setPrice(199 ); p.setColor("土豪金" ); System.out.println(p.getBrand()+"---" +p.getPrice()+"---" +p.getColor()); } }
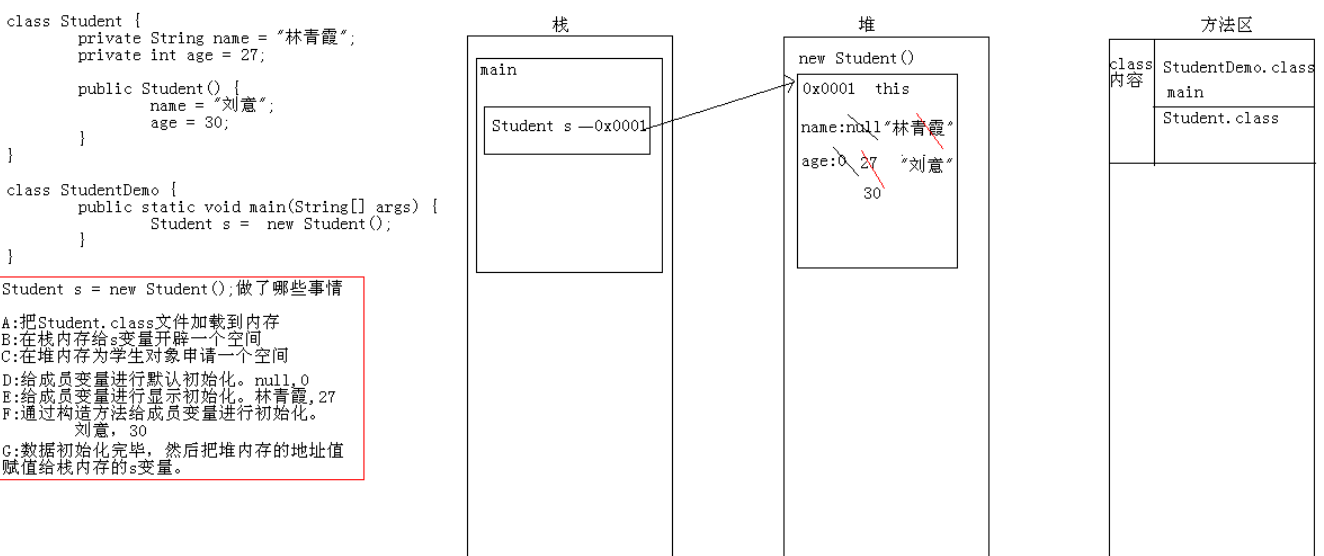
创建对象做了哪些事情 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 (1 )把Student.class文件加载到内存 (2 )在栈内存为s开辟空间 (3 )在堆内存为学生对象申请空间 (4 )给学生的成员变量进行默认初始化。null ,0 (5 )给学生的成员变量进行显示初始化。林青霞,27 (6 )通过构造方法给成员变量进行初始化。刘意,30 (7 )对象构造完毕,把地址赋值给s变量
什么时候定义成员变量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 class Demo int a; int b; public int sum() { return a + b; } } class Test public static void main(String [] args) { Demo d = new Demo(); d.a = 10 ; d.b = 20 ; System.out.println(d.sum()); } }
长方形案例练习 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.util.Scanner;class ChangFangXing private int length; private int width; public ChangFangXing(){} public void setLength(int length) { this .length = length; } public void setWidth(int width) { this .width = width; } public int getZhouChang() { return (length + width) * 2 ; } public int getArea() { return length * width; } } class Test2 public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入长方形的长:" ); int length = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入长方形的宽:" ); int width = sc.nextInt(); ChangFangXing cfx = new ChangFangXing(); cfx.setLength(length); cfx.setWidth(width); System.out.println("周长是:" +cfx.getZhouChang()); System.out.println("面积是:" +cfx.getArea()); } }
员工类案例练习 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class Employee private String employeeId; private String name; private int age; public Employee() {} public String getEmployeeId() { return employeeId; } public void setEmployeeId(String employeeId) { this .employeeId = employeeId; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this .name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this .age = age; } public void show() { System.out.println("员工编号是:" +employeeId+"的这个人是:" +name+"的年龄是:" +age); } } class EmployeeTest public static void main(String [] args) { Employee e = new Employee(); e.setEmployeeId("czbk9527" ); e.setName("唐伯虎" ); e.setAge(18 ); e.show(); } }
自己实现加减乘除并测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import java.util.Scanner;class MyMath public int add(int a,int b) { return a + b; } public int sub(int a,int b) { return a - b; } public int mul(int a,int b){ return a * b; } public int div(int a,int b) { return a / b; } } class MyMathTest public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入第一个操作数:" ); int firstNumber = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入第二个操作数:" ); int secondNumber = sc.nextInt(); MyMath mm = new MyMath(); System.out.println("加法结果:" +mm.add(firstNumber,secondNumber)); System.out.println("减法结果:" +mm.sub(firstNumber,secondNumber)); System.out.println("乘法结果:" +mm.mul(firstNumber,secondNumber)); System.out.println("除法结果:" +mm.div(firstNumber,secondNumber)); } }
static关键字的引入 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 static 关键字(理解) (1 )静态的意思。可以修饰成员变量和成员方法。 (2 )静态的特点: A:随着类的加载而加载 B:优先与对象存在 C:被类的所有对象共享 这其实也是我们判断该不该使用静态的依据。 举例:饮水机和水杯的问题思考 D:可以通过类名调用 既可以通过对象名调用,也可以通过类名调用,建议通过类名调用。 (3 )静态的内存图 静态的内容在方法区的静态区 (4 )静态的注意事项; A:在静态方法中没有this 对象 B:静态只能访问静态(代码测试过) (5 )静态变量和成员变量的区别 A:所属不同 静态变量:属于类,类变量 成员变量:属于对象,对象变量,实例变量 B:内存位置不同 静态变量:方法区的静态区 成员变量:堆内存 C:生命周期不同 静态变量:静态变量是随着类的加载而加载,随着类的消失而消失 成员变量:成员变量是随着对象的创建而存在,随着对象的消失而消失 D:调用不同 静态变量:可以通过对象名调用,也可以通过类名调用 成员变量:只能通过对象名调用 (6 )main方法是静态的 public:权限最大 static :不用创建对象调用 void :返回值给jvm没有意义 main:就是一个常见的名称。 String [] args:可以接收数据,提供程序的灵活性 格式:java MainDemo hello world java java MainDemo 10 20 30
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Person String name; int age; static String country; public Person(){} public Person(String name,int age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public Person(String name,int age,String country) { this .name = name; this .age = age; this .country = country; } public void show() { System.out.println("姓名:" +name+",年龄:" +age+",国籍:" +country); } } class PersonDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Person p1 = new Person("邓丽君" ,16 ,"中国" ); p1.show(); Person p2 = new Person("杨幂" ,22 ); p2.show(); Person p3 = new Person("凤姐" ,20 ); p3.show(); p3.country = "美国" ; p3.show(); p1.show(); p2.show(); } }
static关键字的特点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Student int num = 10 ; static int num2 = 20 ; } class StudentDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Student s = new Student(); System.out.println(s.num); System.out.println(Student.num2); System.out.println(s.num2); } }
static关键字的内存图解
static关键字的注意事项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Teacher public int num = 10 ; public static int num2 = 20 ; public void show() { System.out.println(num); System.out.println(this .num); System.out.println(num2); } public static void method() { System.out.println(num2); function2(); } public void function ( } public static void function2() { } } class TeacherDemo public static void main(String [] args) { Teacher t = new Teacher(); t.show(); System.out.println("------------" ); t.method(); } }
main方法的格式详解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class MainDemo public static void main(String [] args) { System.out.println(args); System.out.println(args.length); for (int x=0 ; x<args.length; x++) { System.out.println(args[x]); } } }
<
数据库原理及应用上机实验四
JavaSE-Day(6)学习笔记
>